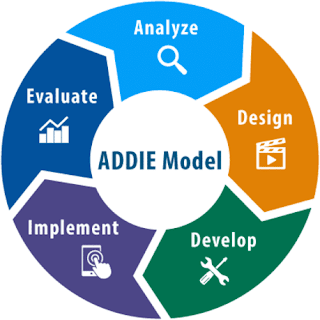
IEDU132 ESE: Design content to transact and evaluate in various contexts of learning environments (Skill, Game, Task, Activity)
What is a learning environment? Learning environment means the varying physical locations, contexts and cultures in which students learn. Since students usually learn in a wide variety of settings like outside of school locations and outdoor environments. The learning environment is a term often used as a more precise or preferred alternative to a classroom, which has a more narrow and traditional implication – for example, a room with desks arranged in rows and a chalkboard. The term also surrounds the culture of a school or class – including how individuals interconnect with one another and how they treat one another. It also involves ways in which teachers organize educational settings to facilitate learning. To name some examples are conducting classes in natural ecosystems which are relevant, using audio, visual and digital technologies. As the qualities and characteristics of a learning environment are determined by a wide range of factors, school policies, governance, s...
